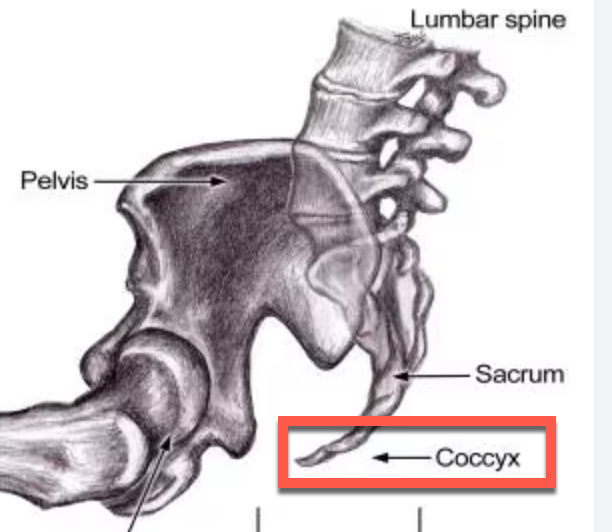
Tailbone pain, also known as coccydynia, is a condition characterized by discomfort in the coccyx, the small triangular bone at the bottom of your spinal column. This pain can arise from various causes such as trauma or childbirth. While often mild and self-limiting, tailbone pain can sometimes require medical intervention for relief.
Key Takeaways
- Tailbone pain can result from trauma or childbirth and can vary in severity from mild to debilitating.
- Diagnosis of tailbone pain typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including physical examination and diagnostic imaging.
- Management options range from conservative treatments like medication and physical therapy to more invasive procedures such as injections or surgery (coccygectomy).
Etiology and Risk Factors of Tailbone Pain
Trauma and Injury
Tailbone pain, also known as coccydynia, is often caused by a noticeable injury, such as falling backward and landing on your tailbone. Such a fall can bruise, dislocate, or break your tailbone. The pain can also result from injuries from repetitive strain, which can occur during activities like bicycling or playing sports. Tailbone injuries may result in a bruise, dislocation, or fracture (break) of the coccyx and cause a lot of pain and discomfort.
Childbirth and Pregnancy
Pregnancy and childbirth are significant risk factors for tailbone pain. During childbirth, the coccyx can be injured due to the pressure exerted as the baby passes through the birth canal. Additionally, the hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to relaxation of the ligaments around the coccyx, making it more susceptible to injury. Tailbone pain can also result from sitting for long periods, especially on hard or narrow surfaces, which places additional pressure on the coccyx.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Symptoms and Signs
Tailbone pain, or coccydynia, can manifest as a dull ache or a sharp pain at the bottom of the spine. Patients often report increased discomfort when sitting for prolonged periods. The pain may radiate to the lower back and hips, exacerbating with activities such as sitting, standing, or transitioning from sitting to standing. In some cases, the pain can be severe enough to interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is essential for diagnosing coccydynia. The examination typically begins with an inspection of the patient’s posture and gait. Palpation of the coccyx area may reveal tenderness, and patients might exhibit pain upon sitting or rising from a seated position. Additionally, the examination may include an assessment of the lumbar and sacral regions to rule out other potential sources of pain, such as facet joint arthritis.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of coccydynia and ruling out other conditions. Plain radiographs of the coccyx can help identify fractures or dislocations. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is particularly useful for visualizing soft tissue injuries and bony injuries to the coccyx. In some cases, computed tomography (CT) scans may be employed to provide detailed images of the bony structures. Accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing future issues.
Management and Treatment Options
Management and treatment options for tailbone pain, or coccydynia, encompass a range of approaches from conservative measures to surgical interventions. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and underlying cause of the pain, as well as the patient’s overall health and response to initial therapies.
Conservative Management:
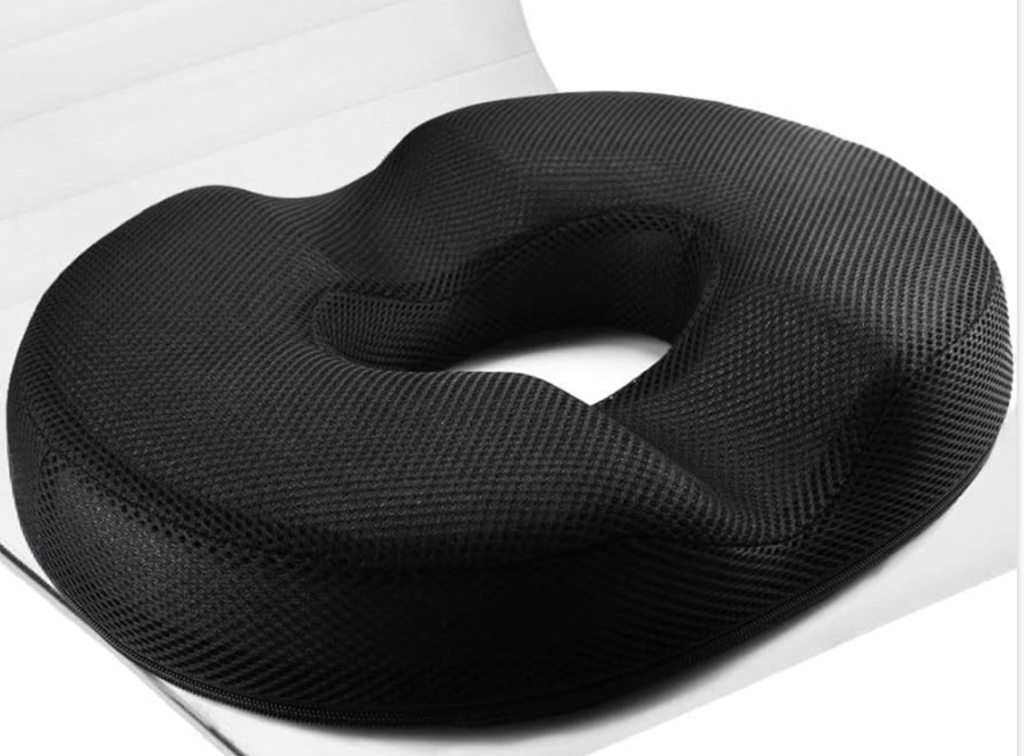
A course of analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatories are helpful to decrease pain and swelling. Sitting on a donut shaped cushion can also alleviate pressure on the coccyx to decrease pain.

Injections:
A steroid injection to the coccyx under imaging guidance can be helpful to relieve pain.
Surgery:
In cases where the coccydynia is severe and unremitting despite medications and conservative therapy, a coccygectomy might be recommended. This is where the painful coccyx is excised through a small incision. There is evidence to show that traumatic coccydynia benefits more from coccygectomy verus non traumatic coccydynia.
About The Author

Dr Gamaliel Tan
Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Spine Surgery in Singapore
Dr Gamaliel Tan is a qualified and experienced spine specialist in Singapore with over 25 years of experience in designing and providing effective solutions for different orthopaedic problems. He specialises in spine surgery and has experience in endoscopic spine surgery and motion preservation spine procedures (artificial disc replacements).
He is a member of the Singapore Spine Society and AOSpine Society.